Health Benefits of Solar PV in California
Written by Amardeep Dhanju
November 24, 2025
The climate benefits of renewable energy are widely recognized, but the benefits to public health are less often discussed. A recent study in One Earth Journal (Imported solar photovoltaic contributed to health and climate benefits in the United States) offers a framework that quantifies the health benefits of California’s use of solar photovoltaic (PV) panels for electricity generation.
In 2024, solar PV installations supplied nearly 30% of California’s electricity demand. The growth of PV solar capacity has displaced conventional generation, particularly natural gas, both in-state and regionally, leading to measurable improvements in public health. According to the journal article, each megawatt of solar generation in California offsets about 0.58 MWh of in-state natural gas generation.
This reduction in gas generation results in substantial reductions in air pollutants, resulting in fewer asthma attacks, heart and lung hospitalizations, and premature deaths. The study also estimates that more than 30 million tons of avoided carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions are attributable to California’s PV build-out over the study period (2014-2022). The study monetized the health benefits of PV solar capacity using the Value of Statistical Life (VSL). VSL translates reductions in mortality risk into monetary terms by measuring a population’s willingness to pay for a small decrease in their risk of death. At the state level, the health benefits equate to roughly $32 per kW of installed PV capacity, and this amounts to approximately $720 million in annual health benefits.
A 2024 report by the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory estimates that levelized cost of energy (LCOE) for utility-scale solar is approximately $46 per megawatt hour (MWh), falling to about $31/MWh with federal tax credits. Using a 24.6% capacity factor and 22.5 GW of installed PV, annual generation is roughly 48.6 TWh. At an LCOE of $31/MWh, this corresponds to an annual energy production cost for solar power of about $1.5 billion. Because the health benefits associated with California’s PV generation are estimated at $720 million annually, these health benefits amount to roughly half the annual cost of generating PV solar electricity. This benefit adds to the other important benefits of solar PV: climate change mitigation, reduced fuel price risk, and enhanced climate resilience.
Bottom line: While renewable energy has been developed primarily to counter the effects of global climate change, California’s PV build-out delivers substantial health returns, on the order of hundreds of millions of dollars annually. In addition, it reshapes regional power flows and cutting fossil generation both in-state and across the west. Doubling down on PV, storage, and grid upgrades, with an equity lens, will amplify these gains and ensure they are felt where they matter the most.
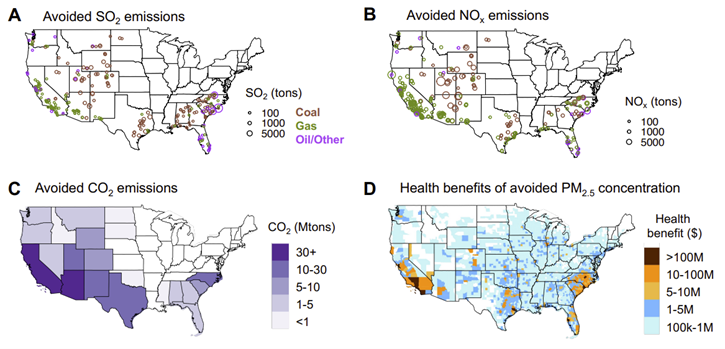
The maps below from the One Earth Journal article show the avoided emissions and PM2.5-related health benefits associated with electricity generation from solar PV.
Panels A and B: Avoided emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrous oxides (NOx) from fossil fuel power plants due to electricity generation from solar PV.
Panel C: Avoided state-level carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions due to electricity generation from solar PV.
Panel D: Health benefits at the county level due to avoided premature mortality associated with exposure to PM2.5 concentrations. The plots show the total cumulative emission changes and health benefits from 2014 to 2022.